What is Bitrate and what does it tell us?
Introduction
In computing - or more specifically in streaming - bit rate, or bitrate, is the number of bits that are transferred or processed per some unit of time. Bitrate is often measured in bits per second (bit/s also bps), where large values are presented with SI prefixes, also known as metric or decimal prefixes:
| Prefix | Unit | Number of bits |
|---|---|---|
| kilobit | 1 kbit/s | 1000 bit/s |
| megabit | 1 Mbit/s | 1.000.000 bit/s |
| gigabit | 1 Gbit/s | 1.000.000.000 bit/s |
| terabit | 1 Tbit/s | 1.000.000.000.000 bit/s |
Note that bps and Bps mean different things. Bits per second (bps) refers to uploading or downloading speed, while bytes per second (Bps) refers to the amount of data transferred.
In practice, bitrate effectively determines the quality level of media (audio or video) that is streamed over the network. In general audio streaming, bitrates are set around 160 kbit/s depending on the encoding and protocol used and are easily handled by most networks today. Video, however, demands much higher bitrates to achieve the wanted quality.
Bitrate in video streaming
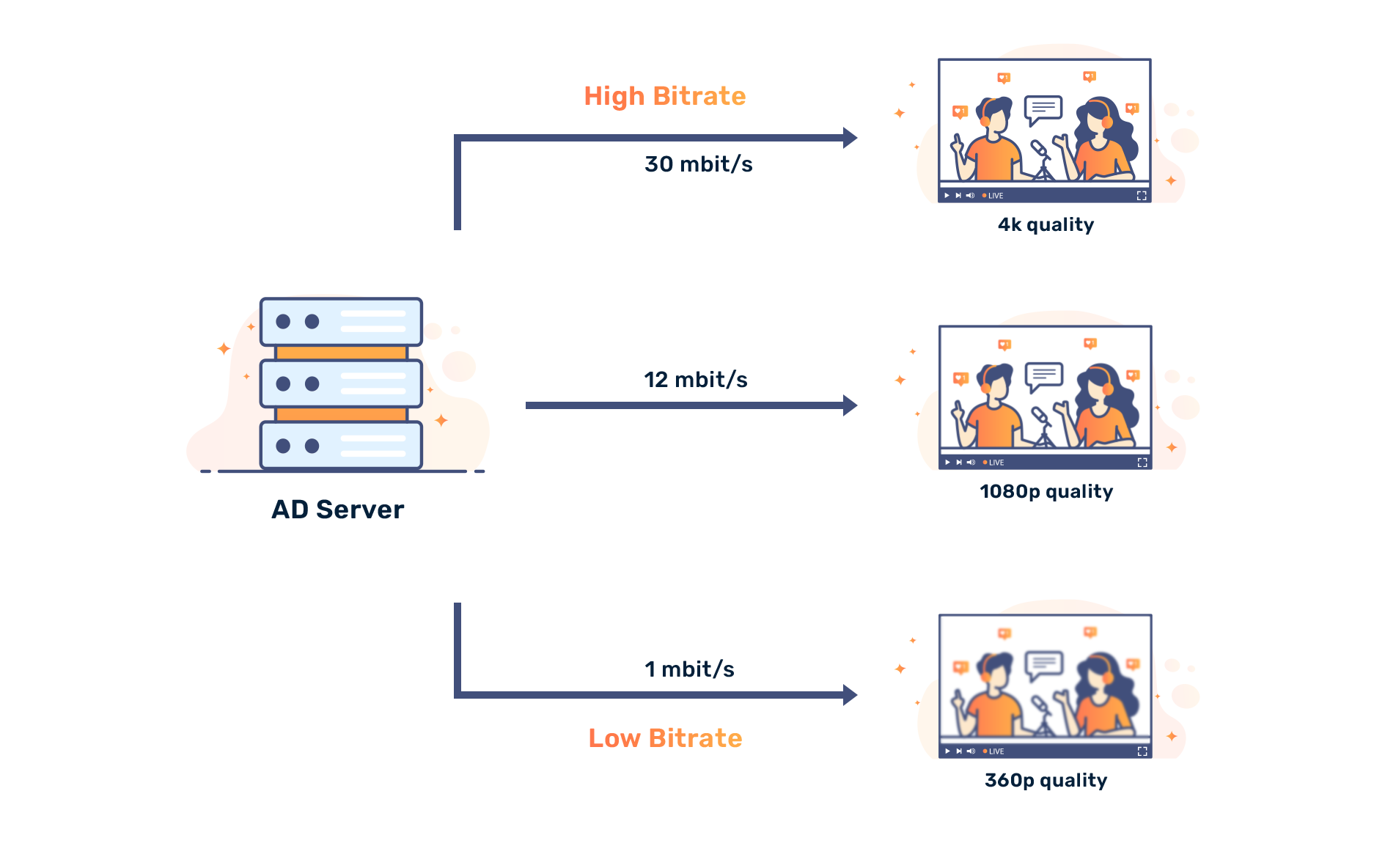
In video streaming, a higher bitrate enables higher image quality in output, due to the higher amount of data being transferred per time unit. The bitrate influences the video file size for local viewing or the minimum necessary network bandwidth of the user for the uninterrupted viewing experience of the streaming video. The following table presents approximate video bitrates for common video presets:
| Type | Resolution | Standard Frame Rate (24, 25, 30) [Mbit/s] | High Frame Rate (48, 50, 60) [Mbit/s] |
|---|---|---|---|
| 360p | 480 x 360 | 1 | 1.5 |
| 480p | 858 x 480 | 2.5 | 4 |
| 720p | 1280 x 720 | 5 | 7.5 |
| 1080p | 1920 x 1080 | 8 | 12 |
| 1440p | 2560 x 1440 | 16 | 24 |
| 2160p | 3860 x 2160 | 35-45 | 53-68 |
Video quality also depends on the use of adaptive bitrate and specific encoding, resolution, and framerate.
- Encoding takes digital video and stores it into a given format using math to find patterns within the video and replaces all the repetitive pieces with references, reducing the size of the file or needed bitrate. Encoding can have lossless compression which allows perfect reconstruction of the original video, and lossy compression which removes the information deemed unnecessary. Generally, when encoding a video, we want to store as much visual data as possible into fewer bits, so lossy compression is preferred. Encoding depends on encoding algorithm settings, algorithm computational complexity, and hardware and software support.
- Resolution defines the number of pixels that form a single video frame. Generally, more pixels bring on a sharper look for the frame. Higher resolutions increase the video quality and improve the viewing experience on larger displays. It is presented with the number of horizontal pixels multiplied with the number of vertical pixels (Width x Height = Total number of pixels -> 480 x 360 = 172,800). The video resolutions for broadcasts and in video players are often represented by only their height (480, 720, 1080...).
- Framerate defines a rate at which the video frames are played to create motion that is represented with frames per second (fps). For most video formats the standard framerate is 24 fps, however, for videos with a high number of fast-moving events higher framerates are advised in the range from 30 to 60 fps.
- Adaptive bitrate is used, when supported by the streaming protocol, to eliminate network bandwidth limits by automatically optimizing the resolution and framerate of video to offer more viewing options. The viewers with higher bandwidth can watch the stream in top quality, whereas viewers with limited bandwidth can reduce the resolution and framerate to match their restrictions.
